Just Relax It 2.0: Expanding Discrete Optimization with New Relaxation Techniques
by Papay Ivan, Vladislav Meshkov, Ilia Stepanov, Vladislav Minashkin
We’re excited to announce the expansion of our Python library “Just Relax It” (relaxit) with three new advanced relaxation techniques for discrete variable optimization. Building on previous release, this version 2.0 introduces REBAR, Generalized Gumbel-Softmax, and Decoupled Straight-Through Gumbel-Softmax algorithms, accompanied by comprehensive experimental validation on reinforcement learning and generative modeling tasks.
What’s New in Version 2.0
Our extended library now includes:
- REBAR (REinforced Bernoulli Rebar) - A control variate method that combines the strengths of REINFORCE and Gumbel-Softmax
- Generalized Gumbel-Softmax - Extends the standard Gumbel-Softmax to arbitrary discrete support values
- Decoupled Straight-Through Gumbel-Softmax - Uses separate temperatures for forward sampling and backward gradient flow
- RELAX Algorithm Implementation - Complete implementation for reinforcement learning with learned control variates
- Experimental Validation - Comprehensive benchmarks on RL environments and VAE-based image generation
New Relaxation Techniques
1. REBAR Relaxation
The REBAR algorithm (Tucker et al., 2017) provides a low-variance, unbiased gradient estimator for discrete random variables by combining the REINFORCE estimator with a continuous relaxation-based control variate.
Key Insight: REBAR uses the Gumbel-Softmax relaxation not as a direct surrogate, but as a control variate to reduce the variance of the REINFORCE estimator while maintaining unbiasedness.
class RebarRelaxation(TorchDistribution):
"""
Rebar continuous Relaxed Bernoulli distribution class.
Implements the REBAR control variate method that combines:
- REINFORCE (score function estimator)
- Gumbel-Softmax (continuous relaxation)
"""
def rsample(self, sample_shape: torch.Size = torch.Size()) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Generate samples using the REBAR reparameterization."""
u = self.uni.sample(sample_shape)
l = self.lambd
t = self.theta
z = torch.clamp(torch.sigmoid(
1/l * ((l**2 + l + 1)/(l + 1)) * torch.log(t/(1 - t)) +
1/l * torch.log(u/(1 - u))
), 0, 1)
return z
Advantages:
-
Unbiased gradient estimates
-
Lower variance than plain REINFORCE
-
Better sample efficiency in RL settings
2. Generalized Gumbel-Softmax
While standard Gumbel-Softmax operates over categorical distributions with one-hot encodings, our Generalized Gumbel-Softmax extends this to arbitrary discrete support values.
class GeneralizedGumbelSoftmax(TorchDistribution):
"""
Generalized Gumbel-Softmax distribution over arbitrary discrete values.
This implements differentiable relaxation of categorical sampling
over arbitrary discrete support values, not just one-hot encodings.
"""
def __init__(self, values, probs=None, logits=None, tau=0.5, hard=False):
self.values = values # Arbitrary discrete support values
self.tau = tau
self.hard = hard
# ... initialization
def weights_to_values(self, gumbel_weights):
"""Project soft/hard weights to scalar values on support."""
return torch.sum(gumbel_weights * self.values, dim=-1)
Applications:
-
Regression with discrete outputs
-
Quantized representations
-
Learning discrete embeddings with meaningful distances
3. Decoupled Straight-Through Gumbel-Softmax
This novel approach decouples the temperature parameter used during forward sampling from that used during gradient computation, providing finer control over the exploration-exploitation trade-off.
class DecoupledStraightThroughGumbelSoftmax(TorchDistribution):
"""
Decoupled Straight-Through Gumbel-Softmax with two temperatures.
Uses separate temperatures for:
- temperature_forward: Hard sampling (forward pass)
- temperature_backward: Gradient estimation (backward pass)
"""
def rsample(self, sample_shape: torch.Size = torch.Size()) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Generate decoupled straight-through samples."""
# Soft sample for gradients (higher temperature)
z_backward = (logits + gumbels) / self.temperature_backward
z_backward = z_backward.softmax(dim=-1)
# Hard sample for forward (lower temperature)
z_forward_logits = (logits + gumbels) / self.temperature_forward
index = z_forward_logits.max(-1, keepdim=True).indices
z_forward = torch.zeros_like(z_backward).scatter_(-1, index, 1.0)
# Straight-through estimator
return z_forward - z_backward.detach() + z_backward
Benefits:
-
Better control over exploration vs exploitation
-
Improved training stability
-
Flexibility in different training phases
RELAX Algorithm for Reinforcement Learning
In addition to the new relaxation techniques, we’ve implemented the full RELAX algorithm (Grathwohl et al., 2018) for reinforcement learning with discrete action spaces.
Algorithm Overview RELAX combines Gumbel-Softmax reparameterization with learned control variates to achieve low-variance, unbiased gradient estimates:
-
Gumbel-Max Trick: Sample discrete actions while maintaining differentiability
-
Control Variates: Learn critic networks to reduce gradient variance
-
Custom Gradient Estimator: Combine score function and pathwise estimators
RELAX Implementation Details
class RELAX(nn.Module):
"""
RELAX policy gradient agent for discrete action spaces.
Combines Gumbel-Softmax reparameterization with learned control variates
to achieve low-variance, unbiased gradient estimates.
"""
def compute_losses(self, action_log_probs, returns, critic_values, critic_z_values):
"""
Compute RELAX gradients:
∇_θ L = (G - V(s,tilde_z)) * ∇log π(a|s) + ∇_θ V(s,z) - ∇_θ V(s,tilde_z)
"""
# Compute advantage for standard policy gradient
advantage = returns - critic_values.detach()
# Accumulate RELAX gradients
for log_prob, return_value, critic_value, critic_z_value in zip(...):
advantage_t = return_value - critic_value
# Gradient of log probability
log_prob_grads = torch.autograd.grad(log_prob, self.actor.parameters())
# Accumulate: ∇log π * advantage + ∇V(z) - ∇V(tilde_z)
all_action_grads = tuple(
accumulated_grad + log_grad * advantage_t +
critic_z_grad - critic_grad
for accumulated_grad, log_grad, critic_grad, critic_z_grad
in zip(...)
)
return actor_loss, critic_loss, all_action_grads
The RELAX gradient estimator provides:
-
Unbiasedness: Unlike direct Gumbel-Softmax approximations
-
Low Variance: Through learned control variates
-
Flexibility: Applicable to any discrete policy gradient setting
Experimental Results We conducted comprehensive experiments across two domains: reinforcement learning and generative modeling.
Reinforcement Learning Benchmarks
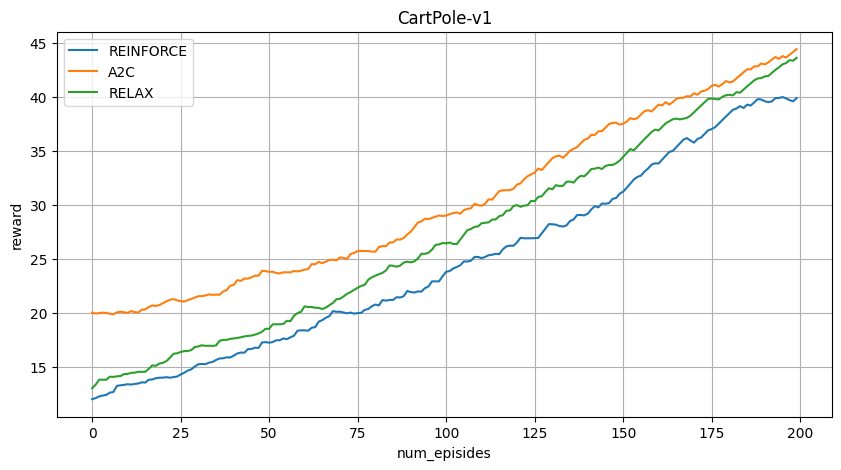
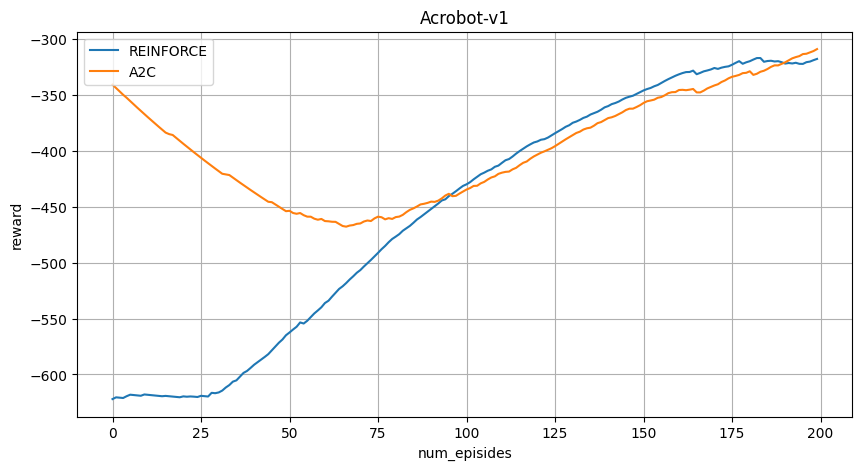
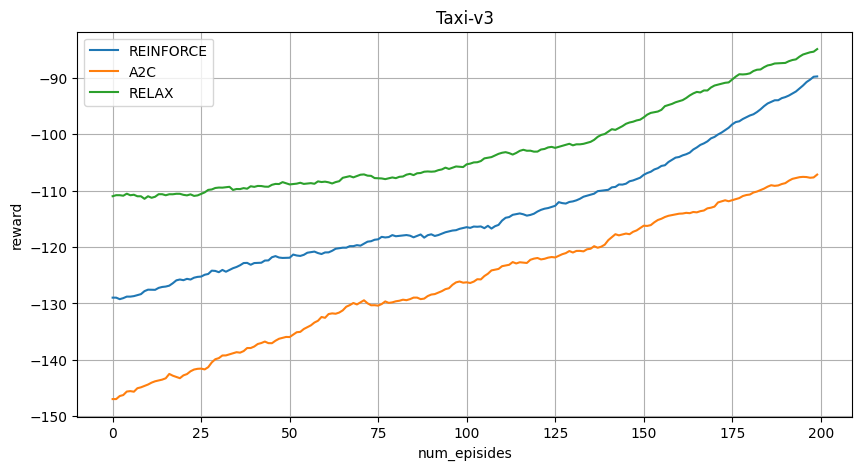
We evaluated the RELAX algorithm on three OpenAI Gym environments:
1. CartPole-v1
2. Acrobot-v1
3. Taxi-v3
VAE with Discrete Latents
For generative modeling, we tested all relaxation methods in Variational Autoencoders with discrete latent variables on MNIST:
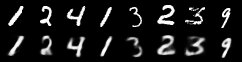
Implementation Architecture
The extended library maintains clean, PyTorch-compatible interfaces:
# Example usage of new distributions
import torch
from relaxit.distributions import (
RebarRelaxation,
GeneralizedGumbelSoftmax,
DecoupledStraightThroughGumbelSoftmax
)
# REBAR for Bernoulli relaxation
rebar_dist = RebarRelaxation(theta=torch.tensor(0.7), lambd=torch.tensor(0.1))
samples = rebar_dist.rsample([10])
# Generalized Gumbel-Softmax for arbitrary supports
values = torch.tensor([-1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0])
probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4])
gumbel_dist = GeneralizedGumbelSoftmax(values=values, probs=probs, tau=0.5)
# Decoupled ST-GS for RL
decoupled_dist = DecoupledStraightThroughGumbelSoftmax(
temperature_forward=0.1,
temperature_backward=1.0,
logits=policy_logits
)
Getting Started Install the extended library from source:
git clone https://github.com/intsystems/relaxit
cd relaxit
pip install -e .
Quick Examples
REINFORCE with RELAX control variates:
from relaxit.rl import RELAX
import gym
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
agent = RELAX(env, hidden_size=128, gamma=0.99)
# Training loop
for episode in range(1000):
reward = agent.train_one_episode(actor_opt, critic_opt)
if episode % 100 == 0:
print(f"Episode {episode}, Reward: {reward:.1f}")
VAE with Generalized Gumbel-Softmax:
from relaxit.distributions import GeneralizedGumbelSoftmax
class DiscreteVAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, latent_dim, num_categories):
super().__init__()
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.num_categories = num_categories
# Define discrete support values
self.values = torch.linspace(-2, 2, num_categories)
def reparameterize(self, logits):
dist = GeneralizedGumbelSoftmax(
values=self.values,
logits=logits,
tau=0.5,
hard=False
)
return dist.rsample()
Conclusion
Version 2.0 of Just Relax It significantly expands the toolbox for discrete variable optimization in neural networks. The new algorithms—REBAR, Generalized Gumbel-Softmax, and Decoupled Straight-Through Gumbel-Softmax—offer improved performance and flexibility across both reinforcement learning and generative modeling tasks.
All methods maintain the core principles of unbiasedness and differentiability
We encourage researchers and practitioners to explore these new techniques, contribute to the library, and share their applications.
Code Repository: click!
Documentation: click!
Previous Version: click!
References
-
Tucker, G., et al. (2017). REBAR: Low-variance, unbiased gradient estimates for discrete latent variable models. NeurIPS.
-
Grathwohl, W., et al. (2018). Backpropagation through the void: Optimizing control variates for black-box gradient estimation. ICLR.
-
Jang, E., Gu, S., & Poole, B. (2017). Categorical reparameterization with Gumbel-Softmax. ICLR.
-
Maddison, C. J., Mnih, A., & Teh, Y. W. (2017). The concrete distribution: A continuous relaxation of discrete random variables. ICLR.
-
Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2014). Auto-encoding variational Bayes. ICLR.
-
Weonyoung Joo, Dongjun Kim, Seungjae Shin, Il-Chul Moon (2020). Generalized Gumbel-Softmax Gradient Estimator for Generic Discrete Random Variables
-
Rushi Shah (2024). Improving discrete optimisation via decoupled straight-through gumbel-softmax
This blog post was written by Papay Ivan. For questions, suggestions, or contributions, please open an issue on GitHub or contact the authors directly.
tags: Relaxation - Gumbel-Softmax - Reinforcement Learning - Python - Library - PyTorch - VAE - REINFORCE - REBAR